The Innovation Awards 2023
Celebrating the pharma industry’s latest developments in drug development and manufacturing technologies. It’s showtime!
| 13 min read | Technology
December is upon us once more – and that means it’s time for The Medicine Maker to showcase the most innovative technologies of the past 12 months.
The list is built on nominations received via The Medicine Maker website – but which innovation leads the rest? It’s up to you to decide. Simply peruse the summaries below and then complete the form available here
Voting will close on March 4, 2024. The winner will have the opportunity to share the story behind their innovation in a 2024 edition of The Medicine Maker.
Without further ado, welcome to the 2023 Innovation Awards!
Cell Shuttle
Fully automated, end-to-end robotic cell therapy manufacturing platform
Cellares

Cellares’ Cell Shuttle robots have been available to some companies previously through an early access scheme, but they are now more widely available. Cell Shuttle robots are self-contained units capable of executing all cell therapy manufacturing processes, including cell enrichment, sampling, selection, expansion, gene transfer, and formulation. According to Cellares, automation of these steps can reduce costs by up to 65 percent, minimize labor and facility space requirements by up to 90 percent, and lower process failure rates by as much as 75 percent. Cell Shuttle technology is also housed within Cellares' integrated development and manufacturing organization Smart Factories, which has the capacity to produce ten times the number of cell therapy batches per year compared with traditional facilities – all within the same physical footprint and workforce. Find out more
CleanCap M6
Capping technology designed to overcome legacy limitations
TriLink BioTechnologies
TriLink says that its CleanCap M6 mRNA cap analog can help developers and researchers maximize the impact of mRNA therapeutics and vaccines, while reducing manufacturing costs. A 5’ cap structure is integral to the stability, expression, and immunogenicity of an mRNA product, but generating a synthetic cap can present manufacturing challenges and inefficiencies. The CleanCap M6 analog improves potency and increases mRNA yields with a capping efficiency of more than 95 percent. Specifically, it produces a natural Cap 1 structure, reducing immunogenicity and increasing mRNA expression by 30 percent compared with legacy capping methods. The technology’s single-pot reaction also requires fewer manufacturing steps, allowing quicker turnaround times, scale-up, and higher transcriptional yields.
As mRNA therapeutic and vaccine pipelines continue to evolve, efficient manufacturing will prove to be critical. Different capping methods impact how efficiently manufacturers can produce a vaccine or therapeutic product because capping reagents influence both downstream and upstream processes affecting cost, time, yield, and purity – all of which affect time to market. Find out more
DynaPro ZetaStar
A nanoparticle analysis instrument with three scattering light techniques
Waters Corporation

Developing LNPs that are both effective and safe requires light scattering techniques to deliver essential and reliable nanoparticle measurements. The DynaPro ZetaStar combines three light scattering techniques in a single device, including Fiber Interferometric Doppler Electrophoresis by Light Scattering (FIDELIS). Unlike conventional light scattering analysis, FIDELIS operates at kHz frequencies to eliminate noise from mechanical disturbances, delivering increased sensitivity and faster measurements (up to tenfold) . The system also uses automated data quality assessments and data capture to enable precise characterization of particle size.
Waters hopes that DynaPro ZetaStar’s ability to characterize particle size by simultaneously conducting dynamic light scattering and electrophoretic light scattering measurements could lead to the development of more stable drug formulations, drug delivery, and enhanced bioavailability. The heightened sensitivity also ensures the detection and characterization of trace substances, enhancing drug safety. Find out more
Enprotect
Two-layer capsule with enteric delivery and acid protection performance
Lonza, Capsules and Health Ingredients

Enprotect is a bi-layer capsule developed to assist in acid protection and enteric delivery of drug modalities. The HPMC inner layer provides the appropriate properties for forming a hard capsule in terms of manufacturing process and mechanical properties, while the HPMC-AS outer layer ensures it opens or disintegrates in the small intestine rather than the stomach – thus providing targeted enteric delivery and protection of the contents from the upper gastrointestinal tract fluids.
According to Lonza, the innovation was made possible by a breakthrough manufacturing platform technology that can produce capsules with two distinct layers while maintaining the standard dimensions of a two-piece hard capsule. The manufacturing method does not require an enteric coating formulation or process parameter. In addition, there is no stress to sensitive APIs because they are filled directly into the capsule without further downstream processing. This generates new possibilities for oral delivery for new classes of APIs and could enable faster to human clinical development because the drug alone can be tested using the Enprotect capsule without formulation studies to evaluate the need for an enteric dosage form. Find out more
EZ BioPacZip
Closed loop powder transfer to minimize the risk of exposure and contamination
ILC Dover

ILC Dover’s EZ BioPacZip is a contained powder handling and transfer technology suitable for buffer and media preparation that builds on the company’s EZ BioPac line. The product, developed through a partnership with Rommelag Flex, creates a fully closed loop to eliminate cross-contamination and operator exposure risks, avoid shedding issues and seal holds, and is designed to be anti-static and anti-dissipative to prevent powder retention.
There is a upper zipper attached to the EZ BioPac, which is single use, and a lower zipper with a canister – a reusable component. When zipped together, the system forms a closed barrier for powder transfer. According to ILC Dover, the zipper overcomes the complexities of using valves, which can be challenging to open and close. Multiple volumes and flange sizes are available, as well as a non-gamma-irradiated and gamma-irradiated version. Custom versions are also available. Find out more
FORMsightAI
CGT development through artificial intelligence and machine learning
Form Bio
FORMsightAI uses AI and machine learning (trained on multiple public and proprietary nucleic acid-based datasets) to help cell and gene developers model billions of potential construct candidates in a swift and safe method. Most cell and gene constructs can be shaped by design choices for 8–10 different key elements beyond the therapeutic gene of interest, so fully exploring the totality of possible vector designs requires the analysis of billions of candidates. Form Bio’s solution delivers the computational capabilities to explore and model the broadest range of vector designs, helping companies to create programs that significantly shorten the critical development stage between early discovery and preclinical regulatory filings. The technology features capabilities for drug product characterization, multi-candidate comparison, bioreactor simulation, gene expression prediction, and immunotoxicity analysis, as well as AI-powered candidate optimization. Find out more
INFINITY MTx PLATFORM
Microfluidics-driven cellular engineering platform for enhanced cell yield and seamless scalability in cell therapy manufacturing
CellFE

Cellular engineering is a critical step in cell therapy, but existing approaches can have limitations. Viral techniques, though dominant, face issues, including high costs, restricted editing capabilities, regulatory obstacles, and safety concerns. On the other hand, non-viral approaches include electroporation – a long-standing method with a number of downsides, including diminished cell health, low yield of edited cells due to its harsh nature, and scalability challenges that delay patient treatment. CellFE’s Infinity MTx platform intends to overcome these hurdles. The Infinity MTx technology is a microfluidic cell engineering platform that performs rapid gene editing through streamlined workflows, whilst ensuring gentle cell treatment, rapid cell recovery, and high yields of healthy cells. This is achieved by leveraging the inherent biomechanical properties of cells, adapting rapidly to their in vivo environment. As cells flow through microfluidic channels at high speeds, they briefly compress while passing under a single ridge. This compression results in a transient reduction in cell size. Within milliseconds of re-expansion, the payload is actively transported into the cell. The design of the microfluidic chip allows for scalability and greater cost efficiencies in cell therapy development and manufacturing. Find out more
MasterControl Advanced Quality Event Management
No-code process quality event management software
MasterControl
MasterControl’s advanced quality event management software is a cloud-native, no-code solution that enables life science quality managers to own and iterate their quality process. Through its combination of highly flexible digital solution and analytics, alongside its no-code functionality, the software allows users to easily modify workflows as processes or regulations change. The software also features automated validation testing with patented “Validation on Demand,” helping to improve compliance with regulatory standards.
MasterControl claims that the technology delivers on the promises of Quality 4.0 initiatives. Quality managers can use the software’s AI capabilities to analyze massive amounts of data to make proactive process improvement decisions. For example, quality managers will be able to access data to improve workflow routing, conduct root cause analysis, and suggest the best mitigation actions. Additionally, quality managers can apply dynamic workflow routing: as certain data is entered, workflows are set based on the conditions.
According to MasterControl, there is currently no other process management tool in the market that uses no-code technology and is purpose-built for the specific needs of life sciences manufacturing. Find out more
Opentrons Flex
Accessible and user-friendly liquid-handling AI-driven lab robot
Opentrons Labworks

The Opentrons Flex is an accessible, user-friendly lab robot designed to accelerate bioautomation and empower scientists to efficiently process multiple samples simultaneously and at a larger scale. The system is built using genomics and proteomics workflows, allowing researchers to automate a wide range of tasks, such as next generation sequencing library preparation, PCR, protein purification, nucleic acid extraction, and precise aliquoting. The vision: to make advanced lab automation more accessible, liberating scientists from the bench and allowing them to focus on the complex challenges in science.
Through the digitization of manual laboratory processes, researchers can now automate a wide range of benchside tasks, ensuring precision and reducing time and costs compared with traditional methods.
According to the developers, the total cost of ownership is just 10 percent that of its competitors. The company also claims that it is the first liquid-handling robot designed to be compatible with “design-of-experiment” programs, including AI-driven agents using large language models. Find out more
Orbitrap Astral Mass Spectrometer
Designed to generate two times deeper proteome coverage and four times more throughput
Thermo Fisher Scientific

Thermo Fisher Scientific claims that the Orbitrap Astral Mass Spectrometer is “one of the most significant advancements in mass spectrometry in 15 years.” The instrument provides up to two times deeper proteome coverage and four times higher throughput compared with current mass spectrometers. It can be used to uncover insights in biology and disease mechanisms from various applications, including single-cell proteomics, quantitative proteomics, and translational proteomics.
The system combines three mass analyzers: a quadrupole mass analyzer for high selectivity and high ion transmission, an Orbitrap mass analyzer for high dynamic range and high-resolution measurements, and the new Astral analyzer for fast and sensitive measurements. The Orbitrap Astral MS expands the scope and statistical power of proteome analysis by analyzing over a million protein groups across 180 samples in a day, measuring more than 8,000 protein groups in each sample, allowing for the discovery of meaningful biological insights with accurate and precise quantities over a larger range. In addition, the system allows high-resolution data-independent and data-dependent acquisition, as well as tandem mass tag-based multiplexed quantification. Find out more
Pin-Point Base Editing Reagents
Reagents to improve access to gene editing
Revvity
Broadening access to base editing was Revvity’s goal when releasing its range of Pin-Point base editing reagents. The reagents can be used in-house across a range of research areas to facilitate genomic insights and cellular therapy research, and includes mRNAs for nCas9 and rat APOBEC, as well as three control guide RNAs designed for knocking out the TRAC, CD52, and PDCD1 loci. Revvity has demonstrated the performance of the reagents in T-cells and pluripotent stem cells.
Pin-Point is one of the few base editing technologies already used in clinical settings, allowing researchers to perform efficient, customisable and off-the-shelf precision nucleotide conversions for single and multiplex gene editing applications. Until now, Revvity claims that base editing reagents were either custom-ordered by end-users or obtained by non-profit laboratories as individual components. The new reagents mean that users can evaluate the Pin-point base editing platform in-house. Find out more
ProteoSuite(SM) Oral
A toolkit to assess the developability of heterobifunctional protein degraders
Catalent
Targeted protein degraders (TPD) could “revolutionize” the field of small molecules, according to Catalent. However, the complex structures and physicochemical properties of TPDs makes satisfactory oral exposure challenging. They also present additional formulation and handling challenges compared with conventional small molecules. Catalent’s ProteoSuite Oral toolkit helps assess the developability of protein degraders, including oral bioavailability. The assessment can be performed even with limited quantities of API, and draws on a range of specialized capabilities to thoroughly evaluate candidate molecules. By providing insight into formulation strategy, the toolkit helps streamline the journey from laboratory development, to clinical application, and beyond. The toolkit builds upon Catalent's expertise with multitudinous protein degrader programs, while tapping into TPD-specific developability models that scrutinize the physicochemical properties and molecular descriptors of these unique compounds. Find out more
RoSS.PADL
Standardized homogeneity and cooling in the aliquoting of pharmaceuticals
Single Use Support

Managing the aliquotation of liquid drugs poses significant challenges because of the diverse viscosities, degrees of sedimentation, and other unique properties inherent to different pharmaceutical liquids. In the case of cell-based suspensions, antibody-drug conjugates, bacterial fermentations, and other similar substances, the lack of homogeneity can result in inconsistent (cell) counts, particle distribution, and active ingredient concentrations within aliquoted single-use containers.
Traditionally, homogenization was a manual process, carrying inherent risks, such as breakages in single-use systems leading to potential contamination, inconsistent filling of bags with varying volumes and sediment concentrations, and unintentional heating of fluids due to manual handling. The RoSS.PADL platform helps ensure standardized homogeneity and cooling in the aliquoting of biopharmaceutical liquids. A kneading mechanism ensures homogenization, facilitating consistent cell counts throughout the filling process into single-use bags. Simultaneously, a cooling element expedites the process while maintaining precise temperature control to prevent reduction in cell viability. Find out more
Sitetrove Diversity Module
Identifying investigators with clinically relevant/demographically diverse patients
Citeline
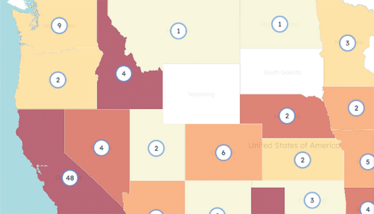
Citeline’s Sitetrove Diversity Module helps with early clinical trial planning, including feasibility and site selection, enabling sponsors and CROs to identify and engage with suitable investigators. At the individual investigator level, the module offers assessments of total unique patient counts, further dissected by race, age, and gender demographics across more than 3,000 diseases, including rare indications. Additionally, Citeline’s accompanying Diversity API allows clients to integrate diversity insights into internal workflows and proprietary metrics for more informed decision-making.
A common goal in the drug development industry is greater patient diversity in clinical trials. It is important to ensure that underrepresented populations are given every opportunity to participate in research and to feel comfortable doing so. Greater diversity in clinical trials leads to better safety, efficacy, and ensures the advancement of life-saving medicines. Find out more
Vertiva
A pre-filled and pre-loaded on-body delivery system
Stevanato Group

According to Stevanato, Vertiva helps improve treatment adherence by providing an enhanced patient experience. The on-body delivery system uses a single-use pod with a prefilled and preloaded 3 mL ISO cartridge, and is suitable for a range of subcutaneous therapies. The system also incorporates a smart, reusable controller that can be pre-programmed to deliver micro-precision basal doses and full-content bolus injections. It can also accommodate different types of primary packaging for larger injection volumes, delivery duration, and user interface. As the controller can be reused, it can help reduce its environmental impact.
The name of the device is taken from the word “versatility” – and Stevanato hopes it will support pharma companies to increase the accessibility of in-home treatment options. Connectivity options also mean that Vertiva is ready for digital health applications. Find out more