Innovation Returns
The Medicine Maker Innovation Awards are back for the second year to recognize the most exciting drug development and manufacturing technologies released during 2016.
Innovation is crucial in any industry, but its impact is perhaps best felt in the pharma, medical and healthcare fields where it saves lives. Ground-breaking new drugs for unmet needs or scientific advances that open the way to new treatment options probably spring to mind first – but let’s not forget the technologies, tools and services that are essential along the way.
2015 marked the birth of The Medicine Maker Innovation Awards, which showcase the most impressive launches over the year. Based on collated comments and rankings from an anonymous judging panel, we presented the Top 10 innovations in our first Innovation Awards – with LEO Pharma’s Open innovation platform taking the coveted top spot (read an update on page 26). For 2016, we’ve decided to crank things up a notch, given the tremendous number of nominations received – many of which caught the eyes of the judges. Here, we present the Top 15 innovations of 2016. Which stars shone the brightest in 2016? Our team of anonymous judges have made their decisions – but do you agree? We welcome your views.
15. FEC40 Capsule Filler
A capsule filler with an output of up to 400,000 capsules per hour

The FEC40 is a compact system for hard capsule filling that uses a patented dual capsule filling process to help boost output to up to 400,000 capsules per hour, without needing to increase the machine cycle time. The capsule filler was developed using the same principles of the company’s double rotary tablet presses. Fette has merged traditionally separate process steps for capsule filling and used the resulting free space for dual arrangement of capsule filling, resulting in an output almost double that of many other machines.
Potential impact:
Capsules are second only to tablets in terms of dosage forms for pharmaceuticals and nutritional supplements. Today, more than 400 billion hard gelatin capsules are produced worldwide every year. Despite these large numbers, Fette says that the output volume of machines used to date is usually around 250,000 capsules per hour.
What the judges say:
“This is a huge output for a capsule filling machine.”
14. TOYOPEARL Sulfate-650F
An ion exchange chromatography resin that binds proteins under atypical conditions

In contrast to many common ion exchange resins, the presence of salt ions can be tolerated during protein adsorption when using TOYOPEARL Sulfate-650F. TOYOPEARL Sulfate-650F is a strong cation exchange resin that exhibits high salt tolerance, while allowing for high-protein binding capacities across a wide range of pH values and conductivities. According to the company, the resin is especially suitable for the purification of therapeutic antibodies.
Potential impact:
Current purification processes frequently require diafiltration or dilution steps before loading the target onto the first ion exchange column. Protein purification with Tosoh Bioscience’s new resin can help potentially shorten and simplify the whole process as physiological salt concentrations can be tolerated during protein binding.
What the judges say:
“By permitting protein adsorption under high salt conditions, this new ion exchange resin may reduce the number of operations during bioprocessing.”
13. Syrina AR 2.25 Auto-Injector
A fully automatic autoinjector for the self-administration of viscous drug formulations
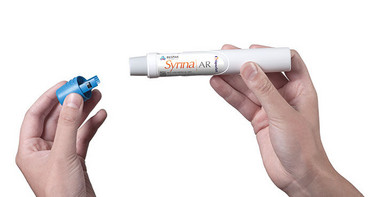
Bespak says that delivering drugs quickly can be a problem for spring-based auto-injectors, especially for viscous formulations. Syrina AR 2.25 is an auto-injector that has been designed specifically for delivering larger volume viscous drug formulations. The device can be used by patients to self-administer their medication and is fully automatic. Based on VapourSoft inhaler valve technology, the autoinjector uses a miniature canister of liquefied HFA gas as its power source to deliver difficult-to-administer formulations in a controlled manner.
Potential impact:
Biologic drugs form an increasing proportion of pharmaceutical pipelines and sales, and most of these will need to be delivered by injection. There is also a drive towards improved patient convenience and a focus on minimizing administration frequency. Syrina AR 2.25ml is a drug delivery device that can do this safely and smoothly.
What the judges say:
“Auto-injectors are a big focus for companies, but this one stands out in being designed specifically for viscous formulations.”
12. PerfeXion
A production quality process to control and monitor glass tubing

When it comes to pharmaceutical primary packaging such as vials, cartridges or syringes, fluctuations in tubing dimensions can have a significant impact on the container performance. Traditionally, manufacturers of glass tubing have monitored quality parameters on a random sample base, but Schott believes there is a better solution. The company has developed a new production quality process. PerfeXion allows for more accurate monitoring – and closer control of – the glass tubing later converted into primary packaging containers. Various interacting online inspection devices, in combination with integrated data collection and data analysis, allow all relevant quality parameters of the original tube to be ideally adapted to the container format (syringe, cartridge, vial or ampoule) and customer specifications.
Potential impact:
PerfeXion is a way of setting the foundation for subsequent steps in the production of pharmaceutical packaging containers. The process targets quality requirements and allows for a customization of specific parameters. Fluctuations in critical glass tubing dimensions can be reduced, which Schott believes will lead to a more constant gliding force of syringe plungers and higher dosage accuracy of multidose cartridges.
What the judges say:
“The quality of syringes and other primary drug packaging is crucial – this process could help prevent some of the quality problems associated with glass, which are too often seen in industry.”
11. Q Exactive BioPharma
Three optimized workflows for comprehensive biopharmaceutical characterization in a single platform

Thermo Fisher Scientific says that the Q Exactive BioPharma MS/MS Hybrid Quadropole-Orbitrap mass spectrometer takes advantage of the high-resolution, accurate-mass (HRAM) capabilities of the company’s popular Orbitrap mass analyzer to enable three key protein characterization workflows: denatured and native MS intact analysis, subunit and top/middle-down analysis, and peptide mapping. The system also features a high mass range mode that adds the ability for intact monoclonal antibody and antibody-drug conjugate analysis, under both native intact and denatured intact conditions, to the existing capabilities for subunit top/middle-down and peptide mapping analysis.
Potential impact:
Researchers require multiple mass spectrometry techniques to perform experiments around biopharmaceutical structure characterization. This system brings a number of Thermo Scientific technologies together into one system that can be used to analyze antibody-based biologics at the intact, subunit, and peptide levels.
What the judges say:
“This system provides a very broad range of high-quality data for protein characterization and addresses critical needs of biologics manufacture.”
10. Golden Number
Universal identifier to help identify persons and facilities involved in clinical research

Study planning and site identification for clinical trials, according to DrugDev, is not easy. There’s plenty of data out there, but there isn’t a common data model, or a unique identifier needed to link the sources of information resulting in non-enrolling or under enrolling sites, which adds cost and time to the clinical research process. DrugDev has created a data model with standard terminology, lists of values, and a universal identifier for investigators and sites called the Golden Number that allows individual pharma companies and CROs to match and share data across collaborations.
Potential impact:
The lack of a common identifier can result in sub-optimal decisions for study planning, feasibility and site selection. It also can create significant business process inefficiencies in in areas such as data integration and consolidated financial reporting. DrugDev believe that the Golden Number can help reduce the number of non-performing sites, decrease the need for rescue sites, reduce IT time and cost spent on data masters, and improve site engagement.
What the judges say:
“DrugDev are drawing attention to a complex problem that deserves greater recognition and more solutions.”
9. Opadry QX
A flexible film coating that can be applied across a broad range of process conditions
Opadry QX is a film coating system suitable for fast application that is scalable across a range of coating equipment and process conditions. The formulation – based on high solids and low viscosity ingredients – reduces preparation and production time, which increases coating process efficiency and helps reduce costs across all types of equipment, according to the company. Opadry QX also enables the coating of temperature-sensitive active pharmaceutical ingredients.
Potential impact:
Drug makers are always looking for ways to make their manufacturing processes more efficient – particularly with the trend towards continuous processing. Opadry QX is flexible enough to be applied at a range of solids concentrations (20-35 percent), which make it well suited for continuous processing. Moreover, because Opadry QX works well in all equipment types and is robust across a wide range of process airflows and temperatures, it can be used in the different coating equipment types found around the world.
What the judges say:
“A very flexible coating that can ease manufacturing.”
8. Vcaps Enteric Capsules
Enteric Capsules that provide enteric release drug delivery without the need for a functional coating

Capsugel has developed a line of functional capsules that provide intrinsic enteric protection and delayed release without the need for a separate functional (enteric) coating. Pharmaceutically approved cellulosic enteric polymers are incorporated into the capsule shell and the capsules are produced using the conventional pin-dipping capsule manufacturing processes.
Potential impact:
By eliminating the need for enteric coating, Capsugel says that the intrinsically enteric capsules can accelerate preclinical assessments and clinical development for compounds requiring enteric protection and/or delayed release in the upper gastro-intestinal tract. The capsules can also enable the oral delivery of small and large molecules that require enteric protection, but are usually degraded by the heat associated with coating processes.
What the judges say:
“Could potentially enable more rapid and convenient enteric formulation of a broad range of thermosensitive drugs.”
7. Cadence BioSMB
Multi-column chromatography system for purification processes up to 2000L

The Cadence BioSMB process system is a fully scalable, disposable flow path, continuous multi-column chromatography solution – a market first, according to the company. It is designed for easy conversion from an existing process development-scale continuous purification step into a GMP-process scale continuous purification based on feedstreams derived from fed batch bioreactors of up to 2000L. The system features an open platform with eight smaller chromatography columns, integrated single-use pump heads, a valve cassette, sensors and flow path.
Potential impact:
The open platform of the BioSMB process system allows for the use of multiple chromatographic technologies, as well as more efficient use of chromatographic sorbents resulting in smaller column volumes and improved process economics. The eight columns provide flexibility and control, while delivering reductions in chromatographic media use (up to 80 percent). Additionally, the single-use flow path can be replaced in 30 minutes, and the valve system does not require cleaning or validation.
What the judges say:
“This could contribute to increasing the efficiency and decreasing the costs of biologics manufacture.”
6. CSP Activ-Blister Solutions
A packaging solution to control the internal atmosphere of existing individual blister cavities
Activ-Blister protects moisture- and oxygen-sensitive solid dose pharmaceuticals packaged on thermoform-fill-seal and fill-seal equipment. It helps to control the internal atmosphere of existing individual blister cavities by offering moisture, oxygen and combination absorption without the use of adhesives and without changes to the existing footprint of a packaging line. The technology can be incorporated into a wide range of blister packaging formats, including push-through, peel/push, and high barrier foils, including both coldform and thermoform.
Potential impact:
This technology enables pharmaceutical manufacturers and contract packagers to achieve moisture protection without using coldform foils, which can be expensive. It also allows for a smaller blister footprint (around 40 to 60 percent size reduction), and provides clear visibility of the tablet/capsule in the blister cavity. Products normally packaged in bottles with desiccant sachets can now be thermoformed into blister cards, eliminating the added costs associated with gas flush/purge and secondary packaging with sachets.
What the judges say:
“As well as being compatible with a broad range of legacy systems, this packaging has the potential to help reduce costs while increasing stability and shelf life.”
5. OptiForm Solution Suite and OptiForm Solution Suite Bio
Accelerated parallel screening platforms that help match early phase small and large molecules with the best formulation options

OptiForm Solutions Suite and OptiForm Solutions Suite Bio address bioavailability and delivery challenges for both small and macromolecules respectively. OptiForm Solutions Suite employs molecule characterization and five formulation technologies – particle size reduction, lipid formulation, salt form optimization, and solid dispersion, including hot melt extrusion and spray dry dispersion. The platform matches the best formulation technologies to the molecule using accelerated parallel screening – within twelve weeks. OptiForm Solutions Suite Bio is a screening technique specifically for the assessment of oral macromolecule delivery.
Potential impact:
According to the company, around 70 percent of molecules in development suffer poor oral bioavailability. These platforms can help quickly and efficiently identify the most suitable formulation technology and achieve optimal bioavailability for advancement into animal pharmacokinetic studies and future development. For macromolecules, oral delivery may help patient acceptance and compliance versus injection and reach optimal clinical outcome. OptiForm solutions Suite Bio can rapidly screen biomolecules’ potential for oral delivery. By quickly evaluating all best available technologies, innovators could improve R&D productivity and lower costs by rapidly progressing difficult molecules.
What the judges say:
“Being able to bring more oral biologics to market would be a big win for the patient community.”
4. Cadence Acoustic Separator
A technology for continuous clarification of batch cell culture

The technology makes use of acoustic forces to enable the continuous removal of cells and cell debris through the Cadence single-use acoustic chamber – achieving clarification of harvested cell culture fluid for downstream processing. Acoustic forces are applied across a counter-current flow of bioprocess fluid to generate three-dimensional standing waves that trap cells at their nodes. This leads to aggregation and precipitation from suspension, preparing the cells for simple extraction. According to the company, the Cadence Acoustic Separator (CAS) results are very reproducible.
Potential impact:
The system can clarify many types of biologic products, including recombinant therapeutic proteins and mAbs, regardless of variability in particulate concentrations and cell culture density, turbidity and viability. According to the company, CAS enables up to 75 percent reduction of the filtration area and associated buffer volume requirements, leading to cost savings and reduced tank sizes. Additionally, the CAS can be integrated into both semi-continuous and fully-continuous bioprocesses.
What the judges say:
“Its broad applicability, compatibility with continuous processing and potential for savings in terms of buffer use and space requirements make this of wide interest.”
3. Vanquish Flex Binary UHPLC
Fully biocompatible ultra-high performance liquid chromatography system with high throughput capabilities

The Vanquish Flex Binary UHPLC (ultra-high performance liquid chromatography) system is a new addition to Thermo Scientific’s Vanquish UHPLC platform that adds a binary solvent delivery option in the 1000 bar (15,000 psi) performance range. The system has been designed for high-speed, fast gradient applications, and features a binary high-pressure gradient pump with 2 x 3 solvent channels and low gradient delay volume that can deliver high flow rates of up to 8 mL/min. In addition, the system features intelligent sample pre-compression, multiple modes of thermostatting and allows for broad flow rates and temperature ranges.
Potential impact:
Thermo Scientific believes that their system gives analysts the “separation power” to identify very low levels of impurities/metabolites in challenging matrices and to uncover minor post-translational modifications. In addition, the use of a high pressure limit and advanced pump technology could help permit rapid sample turnaround and decision making.
What the judges say:
“The Vanquish UHPLC platform is well used and appreciated by industry – this latest system now adds the option for binary solvent delivery.”
“Innovations in UHPLC are making the technology increasingly accessible and easier to use.”
2. SmartDose Platform
Wearable, integrated drug delivery system, for sensitive drug products

The SmartDose platform is a single-use, electronic wearable injector that allows patients to self-administer medication. The device is discreet and placed on the body – usually the abdomen – and has been designed with human factors testing to minimize discomfort. It incorporates a polymer-based drug container (made from Daikyo Crystal Zenith cyclic olefin polymer) with a drug delivery system that can be pre-programmed to deliver high volumes of sensitive drug products. The company says it is particularly well matched for high-viscosity and silicone-sensitive biologic formulations.
Potential impact:
The technology is designed to enable effective delivery of injectable biologics, which can present several challenges for drug packaging and delivery. Many biologics are sensitive, creating potential for interaction with containers and packaging components. Additionally, biologics may require large doses to be injected slowly over time. West believes that the design of the SmartDose platform enables safe, effective and accurate delivery of biologics, while helping to improve the patient experience.
What the judges say:
“Self-administration of biologicals is an important and growing field; systems such as this, which both improve the patient experience and address some of the difficulties of biologics delivery, will no doubt be welcomed by patients.”
“A wearable drug delivery device is highly innovative – and a great leap forward for the field.”
1. Centinel
Gene-editing technology to modify CHO cell lines to be MVM-resistant
Merck KGaA’s Centinel is a gene-editing technology that can be used to modify CHO cell lines to create resistance to minute virus of mice (MVM) – a contamination threat in biopharma manufacturing. The company says the technology was developed after Merck KGaG identified a gene target (Slc35a1) which, upon elimination of expression by gene editing, resulted in a CHO cell line resistant to MVM – while still retaining an equivalent level of protein quality and cell line productivity.
Potential impact:
For biopharma manufacturers using CHO cells, contamination by a small, non-enveloped parvovirus called minute virus of mice (MVM) is a significant threat. To date, most MVM risk mitigation efforts have focused on raw material qualification, viral filtration and inactivation techniques. One of the main challenges with media and cell culture MVM contamination, however, is that it typically eludes detection until the virus has had a chance to infect a cell and multiply. The first signs of contamination may include a drop in viable cell count or a decrease in recombinant protein production. Although infrequent, infection of a fermenter can be catastrophic for a producer, resulting in the loss of product, temporary withdrawal from the market and extensive clean down costs.
Given that CHO-based animal component free (ACF) systems are currently responsible for producing billions of dollars’ worth of therapeutic products every year, adding MVM resistance to a CHO bioproduction cell line could provide an added layer of defense against virus-induced catastrophic failure in animal-component free fermentation systems.
What the judges say:
“This technology could solve an important challenge in the industry.”
“A practical and innovative application of gene-editing technology to enhance biomanufacturing.”
“MVM is a significant problem in biopharma manufacturing that creeps up again and again – and is hard to detect before it’s too late.”

Making great scientific magazines isn’t just about delivering knowledge and high quality content; it’s also about packaging these in the right words to ensure that someone is truly inspired by a topic. My passion is ensuring that our authors’ expertise is presented as a seamless and enjoyable reading experience, whether in print, in digital or on social media. I’ve spent fourteen years writing and editing features for scientific and manufacturing publications, and in making this content engaging and accessible without sacrificing its scientific integrity. There is nothing better than a magazine with great content that feels great to read.