Innovation Strikes Back
The Medicine Maker Innovation Awards, now in their third year, celebrate the most exciting drug development and manufacturing technologies of 2017
Every year, a diverse array of equipment and technologies are released to aid pharma and biopharma manufacture. Which technology stars shone the brightest during 2017? The Medicine Maker has been collecting nominations for months and the judging process is complete. Here, in alphabetical order, we present the top 15 innovations of 2017.
But which technology is the most be innovative? The grand winner of the 2016 Innovation Awards was Centinel – a CHO cell line resistant to minute virus of mice. You can read the story behind this innovation HERE.
We will be sharing the story behind one of our 2017 Innovation Award winners in a 2018 issue of The Medicine Maker – and it’s up to you, our readers, to vote on which 2017 innovation you want to read more about! Vote for your favorite innovation at: http://tmm.txp.to/2017/innovationwinner.
AFG 5000
Accurately dosing and filling both large and small amounts of powder

Flexibility is the name of the game when it comes to the AFG 5000, with its range of versions and features. The number of filling stations can be individually selected, which leads to an output of up to 480 vials per minute in the high-performance range. Bosch has also developed a new variable transport system that continuously feeds vials into the machine, while adjusting its speed precisely to the rhythm of the individual workstations, such as filling, weighing and stopper insertion, to help avoid idle time or bottlenecks.
Potential impact:
Every centimeter in class B cleanrooms counts in terms of operating, maintenance and cleaning costs. The AFG 5000 has been designed to reduce the amount of space that has to be cooled and cleaned with sterile, dry air. In addition, the high output and few parts help accelerate format changes, leading to the potential for more efficient processes and additional savings in space and costs.
Cadence Inline Diafiltration Module
A tangential flow filtration diafiltration device allows for ≥ 3-log removal in a single-pass, continuous operation

The Cadence Inline Diafiltration (ILDF) Module is designed for continuous processing, in-process buffer exchange or contaminant removal in a number of applications. Modules are available with either Delta regenerated cellulose or Omega polyethersulfone membranes to provide high flux, high selectivity and low protein binding characteristics. Pall notes that the modules enable significantly reduced system hold-up volume, and feature an easy to use, holderless design.
Potential impact:
According to Pall, a method for performing diafiltration in a truly continuous, single-pass mode of operation does not currently exist. Instead, diafiltration must be conducted as a batch operation, or in a semi-continuous operation that requires some level of recirculation. The Cadence ILDF device could bring the biopharma industry one step closer to implementing an end-to-end integrated, continuous bioprocessing platform.
Eshmuno P anti-A & Eshmuno P anti-B resins
Improving patient safety by removing key contaminants from plasma-derived therapies

Eshmuno P anti-A and Eshmuno P anti-B are two affinity-based chromatography resins that help remove anti-A and anti-B isoagglutinin antibodies from plasma-derived immunoglobulins (Ig) – without negatively impacting process economics; the resins can be reused for at least 200 cycles, using acid or alkaline cleaning. The resins are manufactured using a combination of the company’s base matrix technology and a novel synthetic approach. The resins are released by a specific test method that evaluates performance with less variability compared with classical agglutination methods.
Potential impact:
Plasma-derived Ig therapies are used to treat a variety of diseases, but trace amounts of anti-A and anti-B isoagglutinins have been associated with increased patient risk for hemolysis. Typically, human plasma is obtained by pooling the plasma of multiple donors of all blood group types, and therefore contains both anti-A and anti-B antibodies. Even using traditional filtration and purification methods, residual trace amounts of anti-A and anti-B blood group antibodies can remain. Eshmuno P resins could help mitigate this risk.
HakoBio
A 3D and digital reality space for simulating and optimizing industrial processes and plants

HakoBio was previously used exclusively by Pall Life Sciences, but the technology was commercially launched in 2017, with users now including the UK’s Cell and Gene Therapy Catapult, Sanofi, and Beckman Coulter. HakoBio is a simple web application that allows users to create processes or design labs, and then view the creation – and assess ergonomics – using virtual reality. Users can select from a vast array of biopharma technology (including specifications and functionalities) modelled in realistic 3D, which can be dragged and dropped to ensure it fits your lab. The interface can also be used for cost and flow simulations, as well as training and data management.
Potential impact:
The platform can be used to easily simulate different processes and factories to get an idea of what may fit in a facility, without needing to consult experts. Creations can also be shared with colleagues. OUAT! believes that HakoBio will facilitate the digital transformation of manufacturing and the switch to Industry 4.0, by providing a visual interface to allow configuration of an Internet of Things platform.
H3N2 Challenge Virus
An influenza virus that can be used as a challenge agent to emulate wild-type infection
This influenza challenge agent has lineage from the seasonally epidemic, non-haemagglutinating H3N2 viruses that arose in the 2010-2011 influenza season, and that have come to predominate since 2014-2015. Thus, the H3N2 Challenge Virus represents one of the most common current circulating strains of influenza of a pandemic origin and can be used for testing the H3N2 portion of prospective prophylactic and therapeutic vaccines. It shows clear and progressive symptomology characteristics of a mild influenza-like illness. Previous influenza challenge agents can demonstrate egg-adaptation and amelioration of disease (both infectivity rates and viral shedding).
Potential impact:
When seeking FDA approval for a vaccine, manufacturers require proof of real-world efficacy, which can be achieved in studies in the community; however, the trials are expensive and the low rates of infection can lead to the need for an enormous patient pool. A challenge agent with a high infection rate – used in conjunction with controlled, human infection studies – could help reduce reliance of efficacy programs on the seasonal incidence of influenza. The efficacy of the vaccines can be determined directly by measuring both virological and host (clinical) endpoints. Maintaining the safety of subjects, whilst maximising data relevance (quality), allows informed go/no go decisions to be made earlier in the pipeline development cycle.
iQ
Standardizing different drug containers to run on the same filling line

The iQ platform standardizes ready-to-use (RTU) syringes, vials and cartridges within a single tub format to run on the same filling line. By standardizing the format, pharma manufacturers can fill various drug/container configurations on the same filling line with only a few minutes of changeover in between. Schott has collaborated with a number of companies during the development of iQ to make the platform compatible with over 30 machines from leading and upcoming vendors.
Potential impact:
Drugs today need to be manufactured in increasingly small batches in shorter periods of time, while adhering to higher quality standards. Currently available RTU solutions require drug manufacturers to fit the filling machines to the specific tub format; by standardizing this part of the process, iQ helps to reduce complexity. With the packaging also being fixed in nests, the risk of glass-to-glass contact is minimized. Schott also believes that the platform could ignite more discussion around issues such as glass breakage and particle reduction.
KLV 1360
An automated system for leak detection

The KLV 1360 for vacuum leak detection can measure leaks resulting from hole sizes of less than five micrometers and can achieve an output of up to 600 vials per minute by using inspection chambers that test groups of vials. The system features an integrated robot system and uses automatic individual re-inspection, which only rejects leaky vials within a conspicuous group. Reference samples help continuous internal process control to ensure maximum testing reliability.
Potential impact:
Leaks in vials can pose a serious risk for patients as the active ingredient may be altered. In particular, non-destructive container closure integrity (CCI) testing technologies are becoming increasingly important in the pharma industry, with the US Pharmacopoeia calling for more quantitative, validated CCI test methods. The KLV 1360 is a sensitive and non-destructive technology that can aid patient safety, while protecting manufacturers against product loss and product recalls.
MabSelect PrismA
An efficient Protein A resin specifically designed to boost mAb purification capacity

According to GE Healthcare, MabSelect PrismA can help mAb producers to improve their purification capacity by up to 40 percent thanks to enhanced binding properties. Protein A chromatography resins play a fundamental role in mAb purification efficiency thanks to their high selectivity, but the drawback is a lack of chemical resistance and the relatively low productivity of many protein A resins. MabSelect PrismA has been developed using high-throughput screening methodologies to identify and resolve weaknesses in the protein A molecule that make it susceptible to sodium hydroxide degradation – allowing MabSelect PrismA to be cleaned with a higher concentration of sodium hydroxide to better control cross-contamination and bioburden risks.
Potential impact:
Historically, the binding capacity of Protein A resins has lagged behind other chromatography resins. GE Healthcare claims that co-optimization of the chromatography bead and the final ligand construct has given MabSelect PrismA a binding capacity on a par with other techniques. Increasing mAb purification capacity can have a significant impact on equipment decisions. If overall productivity of existing equipment is improved, capital investments in new columns and facilities can be delayed until financial risks are reduced. The increased capacity also allows the use of prepacked columns.
Prodigi
Managing serialization requirements with a cloud-based solution
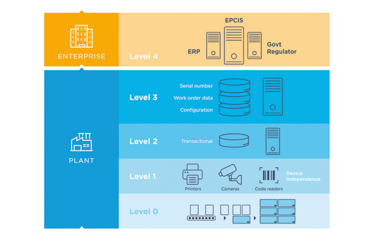
Prodigi is a cloud serialization solution based on the Microsoft Trusted Cloud Azure platform (selected by the European Medicines Verification Organization to build the European Hub). The platform helps pharma companies generate, exchange, manage and analyze serialization data, and also includes a connection interface that facilitates the on-boarding of trading partners by reducing IT resources, connectors and costs.
Potential impact:
Adents has passed the certification process for the European Medicines Verification System (EMVS) – a pan-European system designed so that medicines can be verified at the point of dispensing), meaning that Prodigi can connect securely with the European Hub for the EMVS, and that Adents can now legally vouch for its customers concerning serialization compliance.
The platform meets regulatory requirements regarding unit traceability, but is designed to go beyond compliance to deliver business benefits resulting from the generated data. Serialization data can be structured for business intelligence analysis and serialization data can also be enhanced with external information, such as cold chain monitoring data.
MicroCal PEAQ-DSC
An automated analytical system for characterizing protein stability

Based on differential scanning calorimetry (DSC), the MicroCal PEAQ-DSC analytical system delivers data to guide biopharma development, from protein engineering, through pre-formulation and process development, to formulation and manufacture of the final product. The system provides high throughput, sensitive protein stability analysis with low sample consumption. It is also a fully automated system – all cell filling and cleaning functions can be performed while unattended.
Potential impact:
DSC is a powerful analytical tool for characterizing the thermal stability of proteins and other biomolecules. The technique measures the enthalpy (ΔH) and temperature (Tm) of thermally-induced structural transitions of molecules in solution. This information provides valuable insights into factors that stabilize or destabilize proteins, nucleic acids, micellar complexes and other macromolecular systems. The data can be used, for example, to predict the shelf-life of biomolecular products to enable batch-to-batch and biosimilar versus innovator molecule comparisons.
Q Exactive HF-X Hybrid Quadrupole Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer
Powerful mass spectrometry system to garner greater understanding of biomolecules

Thermo Fisher Scientific’s Q Exactive HF-X Hybrid Quadrupole Orbitrap Mass Spectrometer provides sensitive and reproducible analyses of highly complex samples to help improve the understanding of biomolecules as drug targets, disease markers, and therapeutic agents. The system uses a high-capacity transfer tube for maximum ion loading, an electrodynamic ion funnel that accommodates and transmits ions over a broader mass range, and a high-field Orbitrap mass analyzer. Benefits include rapid and accurate mass analysis, two-to-three-fold sensitivity improvements, and up to an eight-fold improvement in signal-to-noise ratio compared with previous models.
Potential impact:
Harnessing the power of the Orbitrap technology, the new system is designed to help scientists comprehensively profile and quantify the proteome, discover and verify novel biomarkers, and fully characterize complex biotherapeutics. According to Thermo Fisher Scientific, the system was used by Jesper Olsen, associate professor and deputy director of the Novo Nordisk Foundation and Center for Protein Research at the University of Copenhagen, Denmark, to identify 1,100 unique peptides per minute – a new world record.
Valor Glass
Durable glass packaging designed to eliminate delamination

Valor Glass is engineered with higher internal energy than conventional glass packaging and has been developed to address several longstanding challenges with conventional borosilicate packaging. The composition and uniform interior surface of the new containers eliminates delamination, resists damage and breakage, and reduces particulate generation. In addition, the glass is chemically durable with uniform surface chemistry and low extractables, and has been designed to run more smoothly on filling lines at high speeds.
Potential impact:
Valor Glass could offer benefits to both manufacturers and patients. Glass delamination can cause adverse patient events and lead to expensive recalls for manufacturers. Damage introduced on filling lines or during shipping can create sub-visible flaws and cracks in conventional packaging, which could lead to contamination. Valor has been designed to resist cracks and damage during processing and transit, as well as during in-home and clinical settings.
VarioSys Move
An automatic transport system for exchanging production modules and processes

The company’s VarioSys production system comprises custom-fit modules – that can be interchanged at any time – interlinked with a Skan isolator system. VarioSys Move is one of the newest additions to the range. The system that automatically brings machine modules from the parking position to the isolator and back again. It can follow a programed sequence or be controlled by an operator using a remote control to bring the module to the isolator, and from there they are transported automatically.
Potential impact:
The aim behind VarioSys is to provide flexibility via a plug and play format, and VarioSys Move enhances the system with further automation. The right module is guaranteed to be delivered to the right place in the VarioSys line.
VHP DC-A Decontamination Chamber Atmospheric
Atmospheric VHP biodecontamination chambers for safe particulate-controlled material transfer

The concept of minimizing bioburden on the surfaces involved in transfer of material to clean room classified areas is not new but, according to STERIS, such equipment is typically designed as material airlocks equipped with gaseous decontamination equipment. The VHP DC-A Decontamination Chamber Atmospheric series is designed to sterilize the surfaces of various loads in a similar way to steam sterilizers, but by using low temperature vaporized hydrogen peroxide. The system also uses a specific fan design for high airflows to ensure a total cycle time of just 45 minutes, as well as an integrated VHP generation process using continuous humidity control that minimizes peroxide consumption down to 20 ml/cycle.
Potential impact:
The best outcome for aseptic processing is to minimize the particulate amount – and thus risk of contamination – entering clean rooms. Automated systems can help achieve this and STERIS also claims that its VHP decontamination process accomplishes a 6-log bioburden reduction. From an operations perspective, a stand-alone design, with no HVAC connections required, facilitates install and validation
X500B QTOF
Boosting routine biotherapeutic characterization with a benchtop QTOF system

Built specifically for biologics characterization, the X500B High-Resolution Quadrupole Time-of-Flight (QTOF) system aims to boost analytical capacity, simplify workflows and accelerate throughput. SCIEX has designed the system to simplify standard characterization workflows with intuitive software that allows even novice mass spectrometry users to run intact mass and peptide mapping analyses quickly and easily.
Potential impact:
Biotherapeutic protein development depends on efficient product characterization at different parts of the process; liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) techniques are essential in this endeavor. Many LC-MS analyses are now mature enough to be adopted in routine and high-throughput labs. SCIEX believes that the X500B is a streamlined solution that makes the power of mass spectrometry for standard intact mass and peptide mapping workflows accessible to every scientist, regardless of expertise level.

Making great scientific magazines isn’t just about delivering knowledge and high quality content; it’s also about packaging these in the right words to ensure that someone is truly inspired by a topic. My passion is ensuring that our authors’ expertise is presented as a seamless and enjoyable reading experience, whether in print, in digital or on social media. I’ve spent fourteen years writing and editing features for scientific and manufacturing publications, and in making this content engaging and accessible without sacrificing its scientific integrity. There is nothing better than a magazine with great content that feels great to read.